The period from birth to the natural death of an organism represents its lifespan. Every organism has a specific average lifespan. It means every organism grows and lives for a particular length of time. Lifespan may range from one day to 4000 years.
The living organisms do not survive indefinitely on this earth. Every individual dies after attaining a certain age or due to predation, accident, disease or failure to replace molecules to run the machinery of life. The duration between birth and death is called the life span, which may be a few minutes to a few hours in case of some microorganisms or may be several thousand years. The life span of living organisms (both plants and animals) varies greatly.
Plants generally have greater life span as compared to animals. Some perennial trees (e.g., Sequoia) live. for thousands of years. It is because generally the plants continue to grow at their tips even when a large part of their body consists of dead cells (i.e., the cells of cork, sclerenchyma and xylem).
Lifespan
Contents
The life span of an individual generally includes four stages. These are –(1) Juvenility. (ii) Maturity, (iii) Ageing and senescence, and (iv) Death.
(i) Juvenility: This represents the stage when organism develops the capacity to reproduce.
(ii) Maturity: In this stage reproduction starts.
(iii) Ageing and senescence: Progressive deterioration in body of a living being is called ageing. The terminal irreversible stage of ageing is known as senescence.
(iv) Death: In death, there is permanent cessation of all vital activities.
The early period of life span, from the time of birth upto the stage when an organism develops capacity to reproduce, is called Juvenility. Juvenility is followed by maturity during which the organisms reproduce. Gradually the body of organism starts deterioration. This period is called ageing. Ageing terminates into senescence when the deteriorating changes become irreversible. Finally the senescence leads to the death of an organism.
Death causes reduction in the number of individuals of a population which is restored by the addition of new individuals through reproduction. Thus, reproduction is not only production of a new copy like itself, but it is a means for the survival of the population of species on this earth. It is well known that life comes from life. All the living organisms have a property to produce more of its own kind by the process called reproduction.
Lifespan of Animals
| Organism | Life-Span |
| Some Micro-organisms | Few minutes to few hours |
| Mayfly | One Day |
| Cicada | One Day |
| Butterfly |
1-2 Weeks |
| Anagalis (a weed) | 3 Weeks |
| Housefly |
1-4 Months |
| Wheat | 5 Months |
| Jelly Fish |
1 Years |
| Rat | 4 Years |
| Squirrel |
6-8 Years |
| Rabbit | 13 Years |
| Leech |
20 Years |
| Monkey | 26 Years |
| Dog | 20-30 Years |
| Cat |
35-40 Years |
| Whale | 37 Years |
| Ostrich |
50 Years |
| Horse | 60 Years |
| Crocodile |
60 Years |
| Elephant | 65 Years |
| Sea anemones | 78 Years |
| Eagle | 90 Years |
| Man | 100 Years (60.4 yrs. according to World Bank report, 1988-95) |
| Parrot | 140 Years |
| Tortoise | 200 Years |
| Banyan tree | 200 Years |
| White Oak tree | 500 Years |
| Peepal | 2000-3000 Years |
| Sequoia (Red wood tree) | 3000-4000 Years |
| Larrea tridentata Oldest plant found in S.W. California, U.S.A |
11,300 Years |
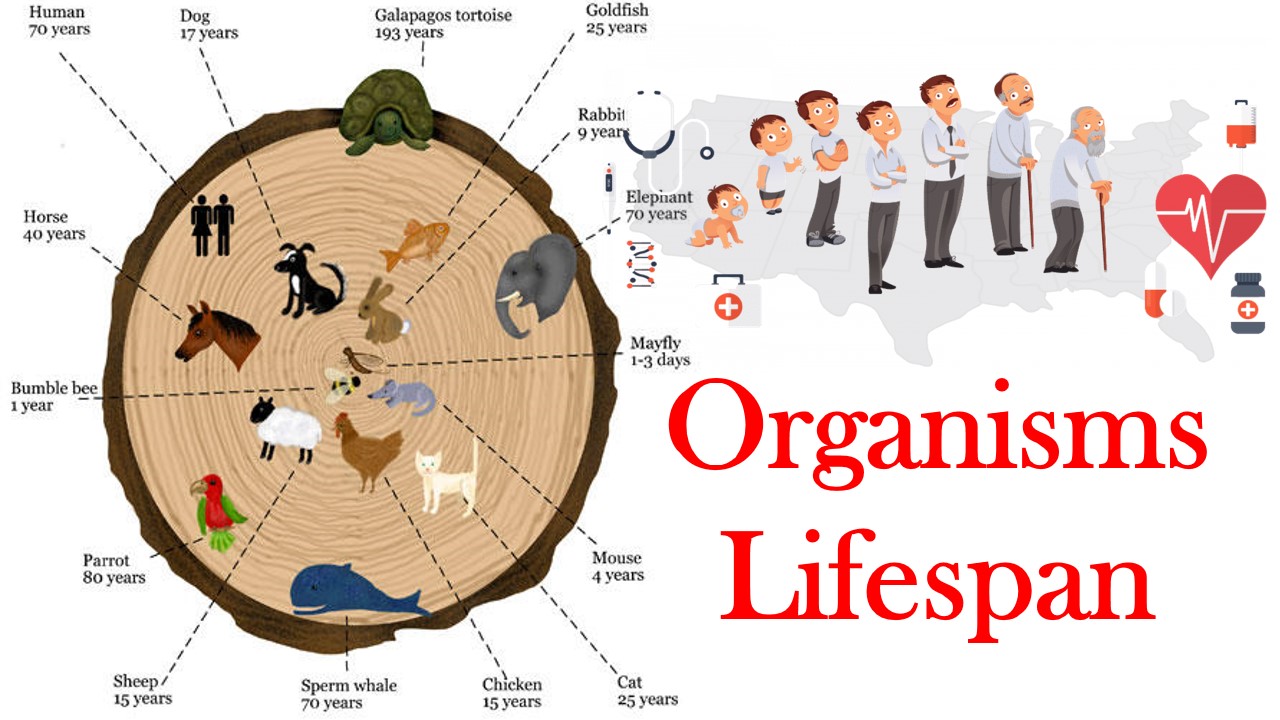
Life Span of few living beings. Different organisms have different lifespans.
Lifespan of Organisms
Lifespan of Mayfly is only one day. Housefly has lifespan of 1-4 months. Lion lives for about 25 years. Insects live for few months. Elephant lives up to the age of 70-90 years. The Banyan tree may live for more than 200 years.
Great Indian banyan tree is located in Indian Botanical garden of Howrah. Similarly, another large and old banyan tree is present at Ketohalli in Bangalore. Butterfly has the lifespan of 1-2 weeks. Tortoise lives up to 150 years. Crow has the lifespan of 15 years. Crocodile lives up to 60 years. Parrot has the lifespan of 150 years.
Here is a categorized list of the lifespans of various animals and organisms, including average durations based on available biological data:
🐾 Mammals
| Animal | Average Lifespan |
|---|---|
| Human | 70–100 years |
| Elephant (African) | 60–70 years |
| Dog (varies by breed) | 10–13 years |
| Cat (domestic) | 12–18 years |
| Horse | 25–30 years |
| Cow | 15–20 years |
| Lion | 10–14 years (wild) |
| Whale (Blue) | 70–90 years |
| Bat (some species) | 20–30 years |
🐦 Birds
| Bird | Average Lifespan |
|---|---|
| Parrot (Macaw) | 50–80 years |
| Pigeon | 5–10 years |
| Crow | 10–15 years |
| Eagle (Bald) | 20–30 years |
| Owl | 10–25 years |
🐢 Reptiles & Amphibians
| Reptile/Amphibian | Average Lifespan |
|---|---|
| Tortoise (Galápagos) | 100–150+ years |
| Crocodile | 70–100 years |
| Snake (Python) | 15–30 years |
| Frog | 5–10 years |
| Gecko | 6–10 years |
🐟 Fish
| Fish | Average Lifespan |
|---|---|
| Goldfish | 10–15 years |
| Betta Fish | 2–5 years |
| Koi Fish | 25–35 years |
| Shark (Greenland) | 200–400 years |
🐛 Insects
| Insect | Average Lifespan |
|---|---|
| Housefly | 15–30 days |
| Mosquito | 2–4 weeks |
| Butterfly | 2–4 weeks |
| Ant (Queen) | Up to 15 years |
| Honeybee (Worker) | 4–6 weeks |
🌱 Plants & Simple Organisms
| Organism | Lifespan |
|---|---|
| Bamboo | Up to 120 years |
| Sequoia Tree | 2,000–3,000 years |
| Bristlecone Pine | 5,000+ years |
| Bacteria (single cell) | Minutes to hours |
| Yeast (Saccharomyces) | Few days to weeks |
| Hydra (simple invertebrate) | Potentially immortal |
⚡️ Notable Extremes
-
🐢 Oldest Animal: Ming the clam – 507 years
-
🦈 Greenland Shark: May live over 400 years
-
🌲 Oldest Tree (Methuselah, CA): ~4,800 years
Would you like this information as a PDF for easy download or sharing?
