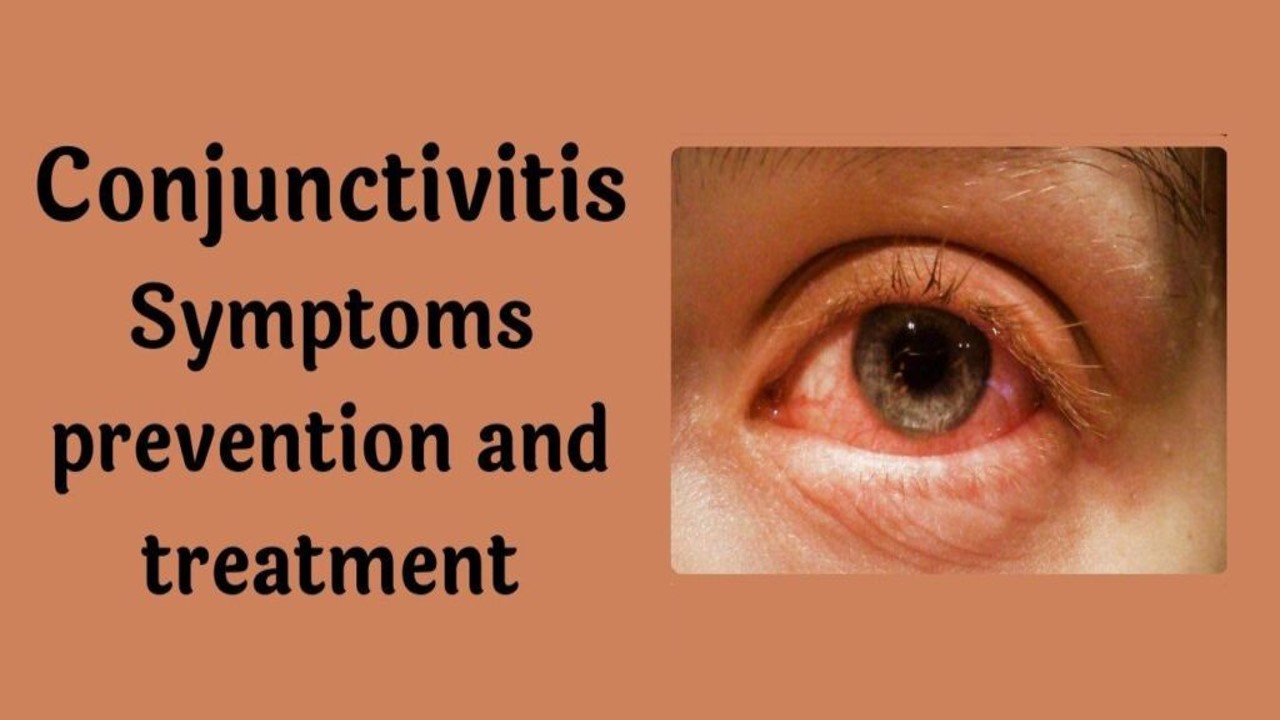
Conjunctivitis – This disease is a common disease that occurs in the eye. Often it is more common in children and less in older people. Conjunctivitis disease is an infectious disease, that is, this disease is a disease spread by infection.
What is conjunctivitis?
Contents
Conjunctivitis is an eye disease. In this disease, the eye becomes very red and along with burning, pain in the eye, itching also starts. Mud and water also fall from the eyes. There is also swelling in the entire eye. In this way, this disease is a very painful disease and the patient remains in a lot of trouble.
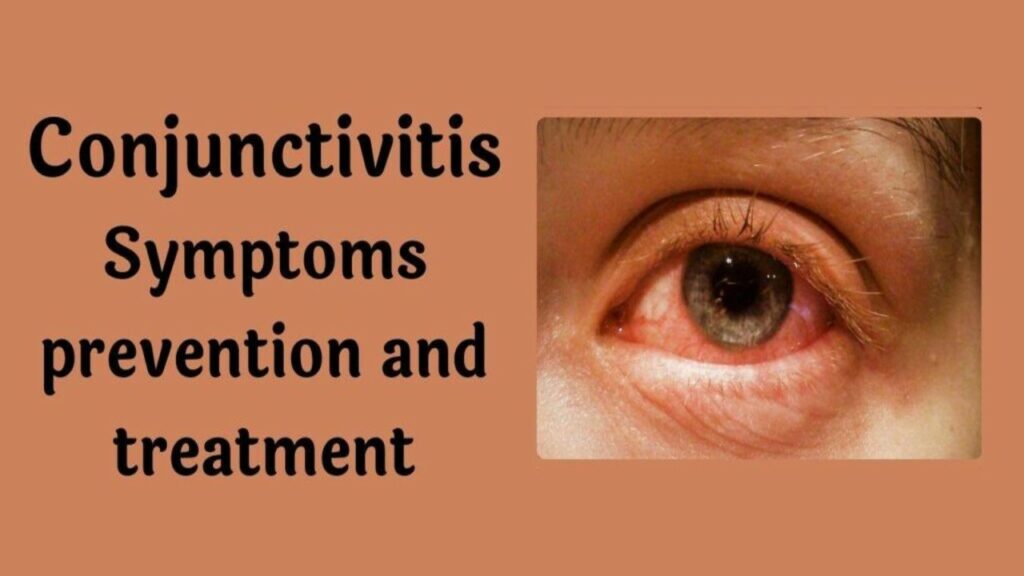
Let us know in which part of the eye this disease occurs. According to the structure of our eye, a part of the eye is the conjunctiva, this disease is a disease occurring in this part of the eye. According to the structure of the eye, the conjunctiva is a transparent membrane located in the sclera and inner part of the eyelid. The same transparent membrane becomes swollen. If you look closely at that swelling, it appears that the blood is filled in the microscopic blood vessels of the membrane.
Causes of Conjunctivitis
Causes of conjunctivitis – This disease mainly occurs due to the following reasons.
(i) Bacterial infection
(ii) viral infection
(iii) Allergies
(iv) Due to the malfunction of the internal organ
What are the symptoms of conjunctivitis?
Symptoms of Conjunctivitis – The symptoms of this disease depend on its cause. I mean that if patients have different reasons for getting it, then their symptoms are also different. All the symptoms are described below –
Symptoms of bacterial infection
When the patient wakes up, he realizes that all of a sudden his eyes are stuck. There is a sticky thick yellow discharge coming out of them. At night, this discharge dries up and becomes a crust and sticks to the eyelids.
eyes turn red
itchy eyes
Symptoms of viral infection
red eyes
get something in the eye
sore throat
eye irritation
watery eyes
swelling of the lymph gland in front of the ear
Symptoms of an allergic infection
watery nose and eyes
Red eyes and swollen eyes
itchy eyes
watery discharge
Symptoms of infection caused by malfunctioning of internal organs
Symptoms of infection affected by heart disease – In this, only the outer and inner corner of the eye remains red.
Symptoms of a lung infection – In this the entire white sclera of the eye is red.
Symptoms of liver infection – In this the whole eye is red. Along with this there is swelling in the eye, watery eyes, hatred of light and pain.
Symptoms of infection affected by the urogenital organ – In this let me tell you that if you are getting it again and again, then it is affected by any of the bladder, prostate, uterus, ovary.
Types of Conjunctivitis
It is of two types
(i) Acute Conjunctivitis (ii) Chronic Conjunctivitis
Symptoms of Acute Conjunctivitis
Eye congestion, swelling and pain
head ache
fever
superficial rapid pulse
Symptoms of Chronic Conjunctivitis
pain and redness of the eyes
photophobia
Prevention of Conjunctivitis
- Wash your hands frequently to avoid spreading the infection.
- Change the patient’s towel, handkerchief, bedsheet, pillowcase every day and clean it daily with warm water.
- Do not use cosmetics.
Pink Eye (Conjunctivitis): Causes, Treatment & Prevention
Overview:
Pink eye, medically known as conjunctivitis, is an inflammation or infection of the conjunctiva — the clear tissue that lines the inside of the eyelid and covers the white part of the eyeball. It is a common condition that can affect one or both eyes and is usually easily treatable.
Causes of Pink Eye
Pink eye can be caused by several factors, including:
-
Viral Infections
-
Most common cause.
-
Often associated with upper respiratory infections (like the common cold).
-
Highly contagious.
-
Usually resolves on its own within 1–2 weeks.
-
-
Bacterial Infections
-
Caused by bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pneumoniae, or Haemophilus influenzae.
-
Can result in more discharge (yellow or green).
-
May require antibiotic eye drops or ointments.
-
-
Allergies
-
Triggered by allergens like pollen, dust mites, pet dander, or mold.
-
Often seasonal.
-
Accompanied by itching, redness, and watery eyes.
-
Not contagious.
-
-
Irritants
-
Caused by exposure to smoke, chemicals, chlorine (from swimming pools), or foreign bodies in the eye.
-
Usually improves once the irritant is removed.
-
-
Newborn Conjunctivitis
-
Can result from blocked tear ducts or exposure to bacteria during birth.
-
Symptoms of Pink Eye
-
Redness in the white of the eye(s)
-
Increased tearing or discharge
-
Itchy or burning eyes
-
Swollen eyelids
-
Gritty feeling in the eyes
-
Crusting over the eyelid or lashes (especially after sleep)
-
Sensitivity to light (in some cases)
Treatment of Pink Eye
Treatment depends on the underlying cause:
-
Viral Conjunctivitis:
-
No specific treatment; supportive care (e.g., warm compresses).
-
Antiviral medications may be used in severe cases (like HSV infection).
-
-
Bacterial Conjunctivitis:
-
Often treated with antibiotic eye drops or ointments.
-
Symptoms typically improve within a few days of treatment.
-
-
Allergic Conjunctivitis:
-
Antihistamine or anti-inflammatory eye drops.
-
Avoidance of allergens.
-
Cold compresses can relieve itching.
-
-
Irritant Conjunctivitis:
-
Rinse eyes with saline or clean water.
-
Avoid the offending irritant.
-
Prevention of Pink Eye
-
Wash hands frequently with soap and water.
-
Avoid touching or rubbing your eyes.
-
Do not share personal items (towels, cosmetics, pillows).
-
Use clean tissues or cloths to wipe your face and eyes.
-
Disinfect surfaces and objects regularly.
-
Change pillowcases frequently.
-
Follow good contact lens hygiene.
-
Avoid swimming in contaminated water.
When to See a Doctor
-
Eye pain or severe redness.
-
Sensitivity to light.
-
Blurred vision that doesn’t improve.
-
Symptoms that worsen or don’t improve in a few days.
-
Signs of a more serious eye infection (e.g., intense pain, swelling, or vision loss).
-
Newborns with eye redness or discharge.
Would you like a printable version of this or formatted as a brochure or infographic?