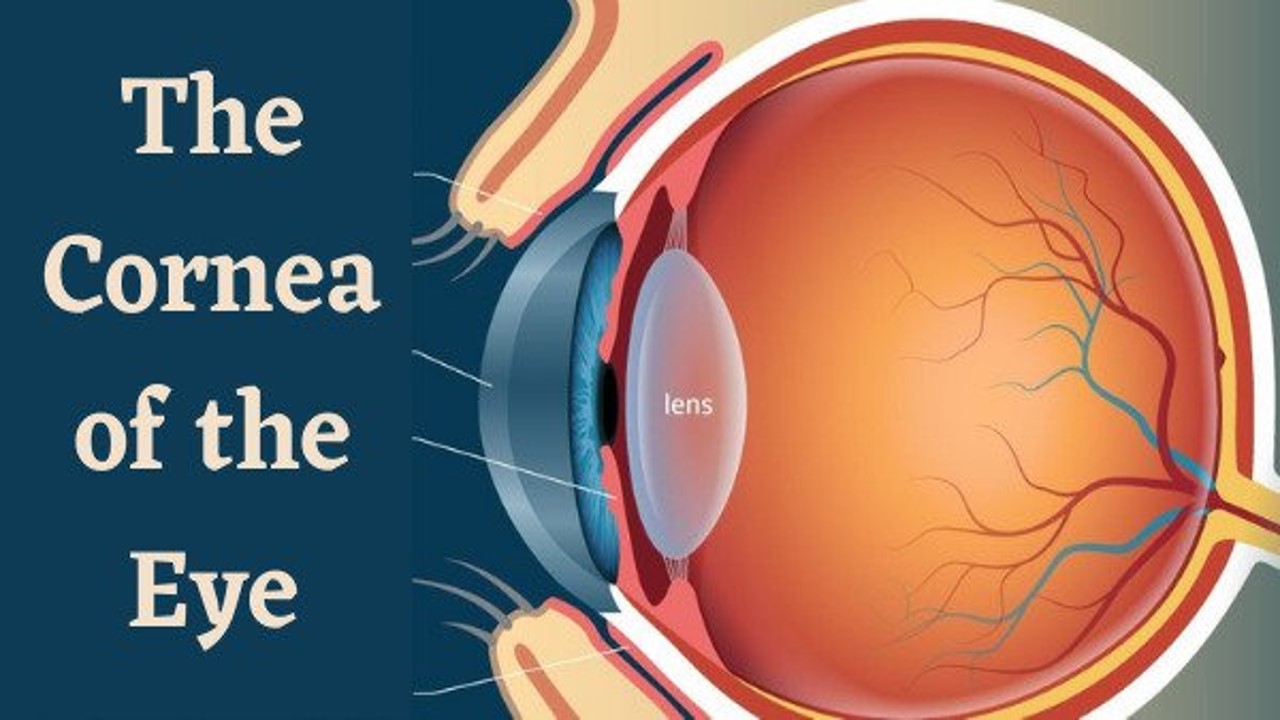
What is the cornea of the eye – The cornea of the eye is an important outer part of the eye, which is completely clear and completely transparent like glass. The cornea in eye is attached to the dark part of the eye.
The Cornea of the eye – Cornea in Eye
Contents
Just as there is a mirror on the clock, in the same way the cornea is placed on the black part of the eye. The structure of the cornea in eye is as follows –
- Its shape is domed.
- It is like a convex mirror.
- Its thickness is 1.2 mm but it is thinner in the middle.
- It has four surfaces.
- This nun is vascular.
- Its degree of curvature varies from person to person. The curvature of the cornea of the eye depends on the intraocular pressure of the eye.
- The cornea is the eye shield.
- The ray of light enters the eye only through the cornea.
- The beam of light that enters the eye helps to focus it on the retina.
Corneal Disease – Corneal Eye
Diseases of the cornea of the eye – The following diseases of the cornea of the eye occur –
- Nebula – A slight clear circular opacity is called a nebula.
- Corneal Opacity – Due to the excessive amount of opaque cornea, blurring becomes more and the object is not seen well. This is called Corneal Opacity.
- Keratitis – Inflammation of the cornea – Inflammation of the cornea of the eye is called Keratitis. Due to this, the patient can see less. It is mainly of the following types.
- Actinic Keratitis – When the cornea reacts to a ray of ultraviolet light and due to which the cornea becomes inflamed, it is called Actinic Keratitis.
- Deep Punctate Keratitis – In this keratitis the cornea becomes inflamed due to syphilis bacteria.
- Herpetic Keratitis – If the cornea of the eye becomes ulcerated or inflamed due to the herpes virus, it is called Herpetic Keratitis.
- Interstitial Keratitis – This keratitis is called Interstitial Keratitis when the cornea of the eye becomes hazier by becoming older, darker.
- Keratitis Bulbosa – When a blister forms on the cornea, the inflammation formed from it is called Keratitis Bulbosa.
- Neurotrophic Keratitis – Persistent corneal inflammation that occurs after Corneal Anesthesia
- Xerotic Keratitis – Inflammation of the cornea caused by drying of the conjunctiva is called Xerotic Keratitis.
Symptoms of corneal disease
- Blurred vision
- Eye pain
- Hate from light
- Redness of the eye
Prevention and treatment of corneal disease
- Consuming a Balance diet that is rich in vitamin A and vitamin C
- Put some good eye drops which are antiviral and anti-bacterial
आँख में कॉर्निया – cornea in Eye in Hindi
कॉर्निया क्या है – कॉर्निया आँख का एक महत्वपूर्ण बाहरी भाग है जो शीशे की तरह पूरा साफ़ और पूरी तरह से पारदर्शी होता है | कॉर्निया आंख के काले वाले भाग पर लगा होता है | जैसे – घड़ी पर शीशा लगा होता है उसी तरह आंख के काले भाग पर कॉर्निया लगा होता है | Cornea का संरचना निम्नलिखित है
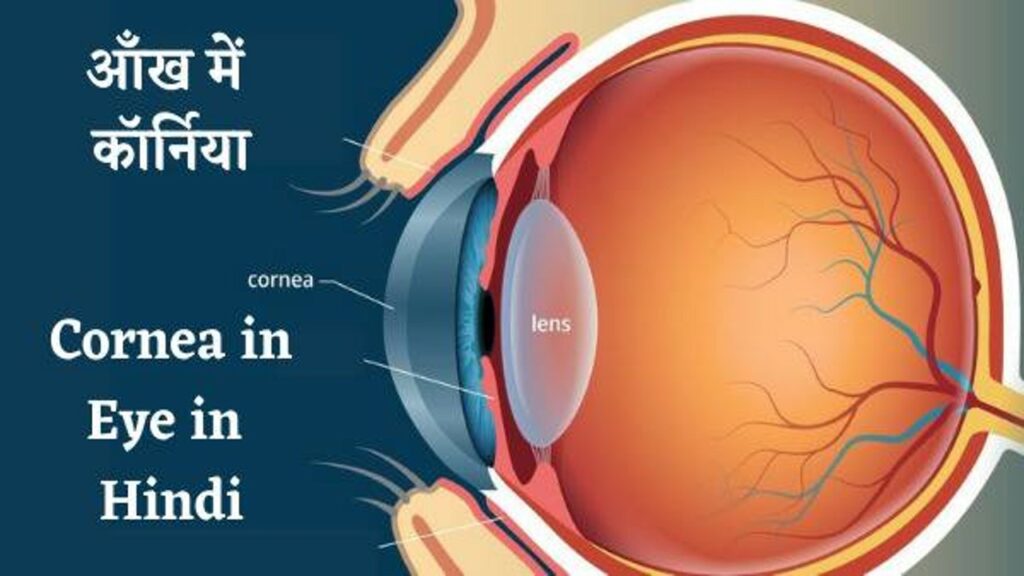
- इसका आकार गुम्बदाकार होता है |
- यह उत्तल दर्पण की तरह होता है |
- इसकी मोटाई 1.2 mm होता है लेकिन बीच में पतला होता है |
- इसमें चार सतह होता है |
- यह नन भास्कुलर होता है |
- इसकी वक्रता की मात्रा प्रत्येक व्यक्ति में अलग-अलग होता है | कॉर्निया की वक्रता आँख के intraocular pressure पर निर्भर करता है |
- Cornea आँख की रक्षा कवच है |
- Cornea से होकर ही प्रकाश की किरण आँख में प्रवेश करती है |
- जो प्रकाश कि किरण आँख में प्रवेश करती है उसको रेटिना पर फोकस करने में मदद करता है |
कॉर्निया के रोग – Cornea in Hindi
कॉर्निया के रोग – cornea के निम्नलिखित रोग होता है –
- Nebula – हल्की सी स्वच्छ मण्डलीय अपारदर्शिता को नेबुला कहते है |
- Corneal Opacity – कॉर्निया के ज्यादा मात्रा में अपारदर्शी होने जाने से धुंधलापन अधिक हो जाता है और वस्तु अच्छे से दिखाई नहीं देता है | इसी को Corneal Opacity कहते है |
- Keratitis – कॉर्निया की सूजन – cornea के प्रदाह को Keratitis कहते है | इसके कारण रोगी को कम दिखाई देता है | यह मुख्यतः तीन प्रकार के होता है |
- Actinic Keratitis – अल्ट्रावायलेट प्रकाश की किरण से जब cornea प्रतिक्रिया कर लेता है और जिसके कारण cornea में सूजन हो जाता है तो उसे Actinic Keratitis कहते है |
- Deep Punctate Keratitis – इस Keratitis में सिफलिस के जीवाणु के कारण cornea में सूजन हो जाता है |
- Herpetic Keratitis – हर्पिस के वायरस के कारण यदि Cornea में अलसर या सूजन हो जाता है उसे Herpetic Keratitis कहते है |
- Interstitial Keratitis – यह Keratitis जब पुराना, गहरा होकर ज्यादा धुंधला (haziness) cornea हो जाता है तो इसे Interstitial Keratitis कहते है |
- Keratitis Bulbosa – कॉर्निया पर जब छाला बन जाता है तो उससे बनने वाले सूजन को Keratitis Bulbosa कहते है |
- Neurotrophic Keratitis – Corneal Anesthesia के बाद होने वाले corneal inflammation बने रहते है
- Xerotic Keratitis – कंजाक्तिवा के सुखी होने के कारण होने वाले cornea के सूजन को Xerotic Keratitis कहते है |
कॉर्निया रोग के लक्षण
- आंख से धुंधला दिखना
- आँख में दर्द
- प्रकाश से घृणा करना
- आंख का लाल होना
कॉर्निया रोग के रोकथाम और इलाज
- पोस्टिक आहार लेना जिसमें विटामिन ए एवं विटामिन स भरपूर मात्रा में हो
- कोई अच्छा ऑय ड्राप जो एंटीवायरल अवं एंटी बैक्टीरियल हो वह डालें
👁️ Corneal Ulcer: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment
A corneal ulcer is an open sore on the cornea, the clear, dome-shaped surface that covers the front of the eye. It is often caused by infections but can also result from trauma, dry eyes, or underlying diseases. If untreated, it can lead to vision loss or blindness.
🔍 Causes of Corneal Ulcer
1. Infections
-
Bacterial (most common, especially in contact lens wearers)
Common pathogens: Pseudomonas, Staphylococcus aureus -
Viral
Herpes simplex virus (HSV), Varicella zoster virus (VZV) -
Fungal
From injury with plant material or in immunocompromised patients -
Parasitic (Acanthamoeba)
Rare, associated with poor contact lens hygiene
2. Non-infectious Causes
-
Dry eyes (exposure keratopathy)
-
Eye injury (trauma, foreign bodies)
-
Chemical burns
-
Corneal abrasions (e.g., from fingernails or improper lens use)
-
Autoimmune diseases (e.g., rheumatoid arthritis)
👁️ Symptoms of Corneal Ulcer
-
Severe eye pain
-
Redness
-
Sensitivity to light (photophobia)
-
Excessive tearing
-
Eye discharge
-
Blurred vision
-
Feeling of something in the eye (foreign body sensation)
-
White or gray spot on the cornea
🩺 Diagnosis
-
Slit Lamp Examination
-
Used to visualize the ulcer under magnification.
-
-
Fluorescein Staining
-
A special dye highlights the ulcer on the corneal surface.
-
-
Corneal Scraping
-
For culture and sensitivity to identify the infective organism.
-
-
Visual Acuity Test
-
To assess the impact on vision.
-
-
Confocal Microscopy (in specialized centers)
-
May help in detecting fungal or Acanthamoeba infections.
-
💊 Treatment of Corneal Ulcer
🔹 Medical Treatment
-
Antibiotic eye drops (broad-spectrum or targeted based on culture)
-
Antiviral drops (e.g., for herpes)
-
Antifungal drops (e.g., natamycin for fungal ulcers)
-
Cycloplegic drops (to relieve pain and prevent muscle spasms)
-
Pain relievers (oral or topical)
⚠️ Steroid drops are not recommended initially, as they can worsen infection—only used under specialist supervision.
🔹 Surgical Treatment
-
Corneal transplant (keratoplasty)
If the ulcer leads to significant corneal scarring or perforation.
🛡️ Prevention Tips
-
Maintain proper contact lens hygiene (never sleep with lenses unless approved).
-
Avoid touching or rubbing the eyes.
-
Treat dry eyes and allergies properly.
-
Use protective eyewear during activities with risk of eye injury.
-
Seek prompt medical attention for any eye injury or persistent redness.
If you or someone you know is experiencing these symptoms, especially with vision changes or pain, consult an ophthalmologist immediately, as delays can result in permanent vision loss.