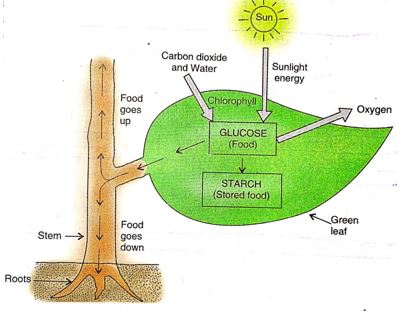
Just like other organisms, plants also require food which can supply energy for their various metabolic activities. Though animals can move from one place to another in search of food, plants just stand still at one place and make their own food. Green plants are autotrophic and synthesize their own food by the process of photosynthesis.
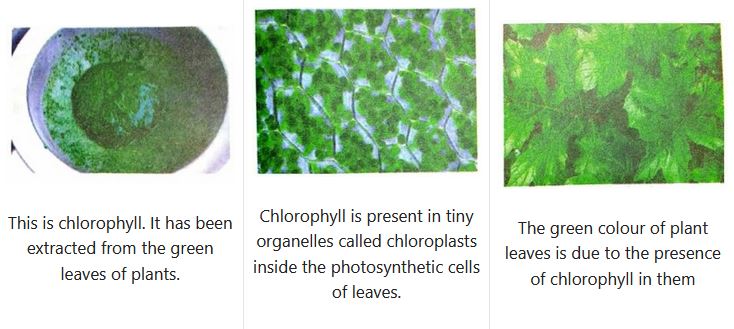
Photo’ means ‘light’ and ‘synthesis’ means ‘to build’, thus ‘photosynthesis’ means ‘building up by light’. The plants use the energy in sunlight to prepare food from carbon dioxide and water in the presence of chlorophyll. Chlorophyll is present in the green coloured bodies called chloroplasts’ inside the plant cells. In fact, the leaves of a plant are green because they contain tiny green coloured organelles called chloroplasts (which contain chlorophyll). Keeping these points in mind, we can now define the process of photosynthesis as follows:
The process by which green plants make their own food (like glucose) from carbon dioxide and water by using sunlight energy in the presence of chlorophyll, is called photosynthesis. Oxygen gas is released during photosynthesis. The process of photosynthesis can be represented as :

The process of photosynthesis takes place in the green leaves of a plant. In other words, food is made in the green leaves of the plant. The green leaves of a plant make the food by combining carbon dioxide and water in the presence of sunlight and chlorophyll. The carbon dioxide gas required for making food is taken by the plant leaves from the air. This carbon dioxide enters the leaves through tiny pores in them called stomata.
Green plants make their own food by photosynthesis
Water required for making food is taken from the soil. This water is transported to the leaves from the soil through the roots and stem. The sunlight provides energy required to carry out the chemical reactions involved in the preparation of food. The green pigment called chlorophyll present in green leaves helps in absorbing energy from sunlight. Oxygen gas is produced as a by-product during the preparation of food by photosynthesis. This oxygen gas goes into the air.
The food prepared by the green leaves of a plant is in the form of a simple sugar called glucose. This glucose food made in the leaves is then sent to the different parts of the plant. The extra glucose is changed into another food called starch. This starch is stored in the leaves of the plant. Glucose and starch belong to a category of foods called carbohydrates. The foods like carbohydrates prepared by photosynthesis contain chemical energy stored in them. Thus, the green plants convert sunlight energy into chemical energy by making carbohydrates (foods).
All these food items have been made by the plants by the process of photosynthesis
The food prepared by photosynthesis provides all the energy to a plant which it needs to grow. And when we eat plant foods (like foodgrains, fruits and vegetables), the chemical energy stored in them is released in our body during respiration.
We will now describe what actually happens during the process of photosynthesis. The photosynthesis takes place in the following three steps:
1. Absorption of sunlight energy by chlorophyll.
2. Conversion of light energy into chemical energy, and splitting of water into hydrogen and oxygen by light energy
3. Reduction of carbon dioxide by hydrogen to form carbohydrate like glucose by utilising the chemical
energy (obtained by the transformation of light energy).
Please note that the three steps involved in photosynthesis need not take place one after the other imediately. They can take place at different times. For example, desert plants take up carbon dioxide at night and prepare an intermediate product which is acted upon by the sunlight energy absorbed by chlorophyll when the sun shines during the next day.
Conditions Necessary for Photosynthesis
Contents
It has been found by experiments that the presence of sunlight, chlorophyll, carbon dioxide and water is necessary for the process of photosynthesis. So, we can say that : The conditions necessary for photosynthesis to take place are
1. Sunlight,
2. Chlorophyll,
3. Carbon dioxide, and
4. Water.
Please note that the conditions necessary for photosynthesis are also the conditions necessary for autotrophic nutrition. We will now describe some experiments to show that sunlight, chlorophyll and carbon dioxide are necessary for photosynthesis by green plants. These experiments will also show that leaves finally make ‘starch’ as food by photosynthesis.
The experiments on photosynthesis depend on the fact that green leaves make starch as food. And that starch gives a blue-black colour with iodine solution. Now, ordinarily all the plants have starch in their green leaves, so before we can use a plant in a photosynthesis experiment, the initial starch present in its leaves must be removed. In other words, we should destarch the leaves of a plant before using it in a photosynthesis experiment. The green leaves of a plant are destarched by keeping this plant in a completely dark place in a room for at least three days.
When the plant is kept in a dark place, it cannot make more starch (food) by photosynthesis because there is no sunlight. So, the plant kept in dark place uses the starch already stored in its leaves during respiration. The plant will use up all the starch stored in its leaves in about three days’ time. So, after about three days, the plant leaves will not have any starch left in them. And we say that the leaves have been destarched. This plant with destarched leaves can now be used in the photosynthesis experiments. Please note that we will be using a plant growing in a pot in these experiments. The ‘plant growing in a pot’ is called ‘potted planť. Let us describe the experiments now.
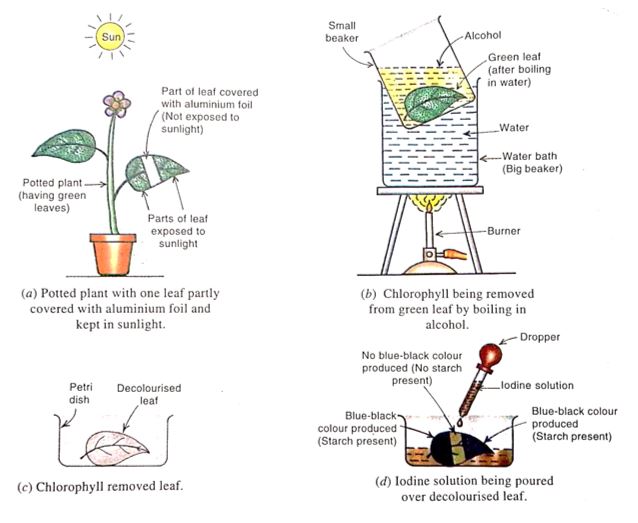
1. Experiment to Show that Sunlight is Necessary for Photosynthesis
1. We take a potted plant having green leaves and place it in a completely dark place for about three days to destarch its leaves. So, in the beginning of the experiment, the leaves do not have any starch in them.
2. Take a thin strip of aluminium foil (or black paper) and wrap it in the centre of one leaf on both the sides (while the leaf is still attached to the plant). The aluminium foil should be fixed tightly to the leaf by using paper clips so that sunlight may not enter it from the sides. The aluminium foil should cover only a small part of the leaf so that the remaining part of the leaf remains uncovered and exposed to sunlight. We have covered the centre part of the leaf with aluminium foil so that sunlight may not fall on this covered part of the leaf.
3. Keep this potted plant (with partially covered leaf) in bright sunshine for three to four days.
4. Pluck the partially covered leaf from the plant and remove its aluminium foil. Immerse this leaf in boiling water for a few minutes. This will break down the cell membranes of leaf cells and make the leaf more permeable to iodine solution (so that it may reach the starch present inside the leaf cells). This leaf is now to be tested for the presence of starch. But before testing for starch, chlorophyll has to be removed from the leaf. This is because chlorophyll interferes in the test for starch due to its green colour.
Experiment to show that sunlight is necessary for photosynthesis.
5. Put the plucked leaf in a beaker containing some alcohol. Place the beaker containing alcohol and leaf in a water bath (A water bath can be a bigger beaker containing water). A water bath is being used here for heating alcohol because alcohol is a highly inflammable liquid. So, if alcohol is heated directly over a flame, then it will catch fire at once.
6. Heat the water in the bigger beaker (or water bath). Then the alcohol in the smaller beaker will also get heated and start boiling soon. This boiling alcohol will extract (or remove) chlorophyll from the green leaf.
7. Boil the green leaf in alcohol till all its green pigment ‘chlorophyll’ is removed. The leaf will now become almost colourless or pale (and the alcohol will turn green).
8. Remove the colourless leaf from alcohol and wash it thoroughly with hot water to soften it and remove any chlorophyll which may be sticking to it.
9. Place the colourless leaf in a petri-dish. Drop iodine solution over the decolourised leaf with the help of a dropper. Observe the change in colour of leaf.
10. The middle part of leaf which was covered with aluminium foil does not turn blue-black on adding iodine solution showing that no starch is present in this middle part of the leaf. This is because sunlight could not reach the covered ‘middle part of the leaf due to which the covered ‘middle part’ of leaf could not do photosynthesis to make starch.
11. The uncovered part of leaf (on both sides of the aluminium foil) which was exposed to sunlight turns blue-black on adding iodine solution showing that starch is present in this part of leaf. This means that the part of leaf which was exposed to sunlight could do photosynthesis to make starch.
12. Since the part of leaf which was covered and hidden from sunlight does not contains starch but the part of leaf which was exposed to sunlight contains starch, therefore, we conclude that sunlight is necessary for photosynthesis (to make food like starch).
From the above experiment, we actually get two conclusions. That:
(i) sunlight is necessary for the process of photosynthesis, and
(ii) leaves make starch as food by photosynthesis.
Most of the common plants have leaves which are totally green (because all the parts of such leaves contain the green pigment called chlorophyll). But there are some plants whose leaves are partly green and partly white. The green part of such a leaf contains chlorophyll but the white part of such a leaf does not contain chlorophyll. The leaves which are partly green and partly white are called ‘variegated leaves’.
Variegated leaves
The plants such as croton and Coleus have variegated leaves which are partly green and partly white. We will use a plant having variegated leaves in the next experiment to show that chlorophyll is necessary for the process of photosynthesis in plants.
2. Experiment to show that Chlorophyll is Necessary for Photosynthesis
1. We take a potted plant like croton whose leaves are partly green and partly white. The green part of the leaf has chlorophyll but the white part of the leaf does not have chlorophyll.
2. Place this plant in a completely dark place for about three days to destarch its leaves.
3. Take out the potted plant from the dark place and keep it in bright sunshine for three to four days.
Experiment to show that chlorophyll is necessary for photosynthesis.
4. Pluck the variegated leaf from the plant, boil it in water for a few minutes and then remove its green colour ‘chlorophyll’ by boiling it in alcohol. The green parts of the leaf get decolourised. So, we get decolourised leaf.
5. Wash the decolourised leaf with hot water to soften it and remove any chlorophyll which may be sticking to it.
6. Pour iodine solution over the colourless leaf and observe the change in colour of the leaf.
7. We will find that the outer part of leaf that was originally white (without chlorophyll) does not turn blue-black on adding iodine solution showing that no starch is present in this outer part of the leaf. From this observation we conclude that the photosynthesis to make starch does not take place without chlorophyll.
8. The inner part of leaf which was originally green (contained chlorophyll) turns blue-black on adding iodine solution showing that starch is present in this inner part of the leaf. From this observation we conclude that the photosynthesis to make starch takes place in the presence of chlorophyll. In other words, chlorophyll is necessary for the process of photosynthesis to take place.
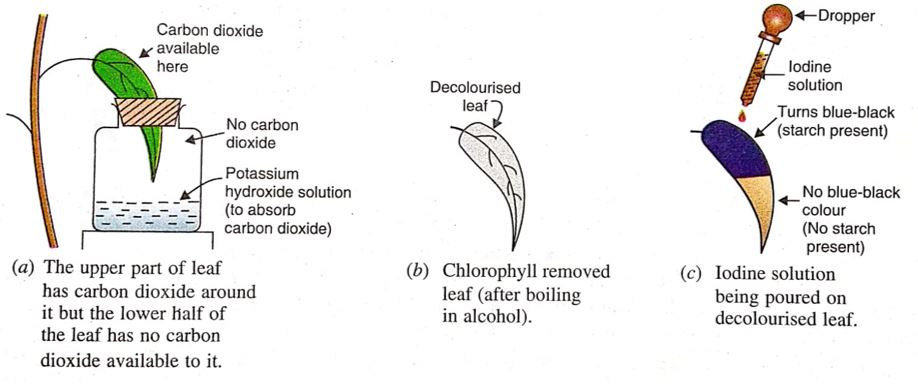
3. Experiment to show that Carbon Dioxide is Necessary for Photosynthesis
1. We take a potted plant having long and narrow leaves and place it in a completely dark place for about three days to destarch its leaves.
2. Take a glass bottle having a wide mouth and put some potassium hydroxide solution (KOH solution) in it. (This potassium hydroxide solution is to absorb the carbon dioxide gas from the air present in the glass bottle so that no carbon dioxide is left in the air inside the glass bottle).
3. Take a rubber cork which fits tightly into the mouth of the glass bottle and cut it into two halves.
4. Put a destarched leaf of the potted plant (while it is still attached to the plant), in-between the two halves of the cut cork and then fit the cork in the mouth of the glass bottle. The upper half of the leaf should remain outside the glass bottle and only the lower half of the leaf should be inside the glass bottle.
5. The potted plant (with its one destarched leaf half inside the glass bottle containing potassium hydroxide solution) is kept in sunlight for 3 to 4 days. During this period, the upper half of the leaf (which is outside the glass bottle) gets carbon dioxide from the air but the lower half of the leaf (which is inside the glass bottle) does not get any carbon dioxide. This is because all the carbon dioxide of the air present in the glass bottle has been absorbed by potassium hydroniue solution. And no fresh air can come into the closed glass bottle.
Experiment to show that carbon dioxide is necessary for photosynthesis.
6. Pluck the leaf from the plant and take it out from the glass bottle. Remove the green coloured chlorophyll from the leaf by boiling it in alcohol. In this way, we get a decolourised leaf.
7. Wash the decolourised leaf with water to remove any chlorophyll which may be sticking to it.
8. Pour iodine solution over the colourless leaf and observe the change in colour of the leaf.
9. We will find that the lower half part of the leaf (which was inside the glass bottle having no carbon dioxide around it), does not turn blue-black on adding iodine solution showing that no starch is present in this lower half of the leaf. From this observation we conclude that the photosynthesis to make starch in the leaf does not take place without carbon dioxide.
10. The upper half part of the leaf (which was outside the glass bottle, having carbon dioxide around it) turns blue-black on adding iodine solution showing that starch is present in this upper half of the leaf. From this observation we conclude that photosynthesis to make starch) takes place in the presence of carbon dioxide. In other words, carbon dioxide is necessary for the process of photosynthesis to take place.
Raw Materials for Photosynthesis
The preparation of carbohydrates (food) by plants by the process of photosynthesis requires two materials (or substances) : carbon dioxide, and water. Thus, the raw materials for photosynthesis are:
1. Carbon dioxide, and
2. Water.
We will now describe how these two raw materials become available to plants for photosynthesis.
1. How the Plants Obtain Carbon Dioxide
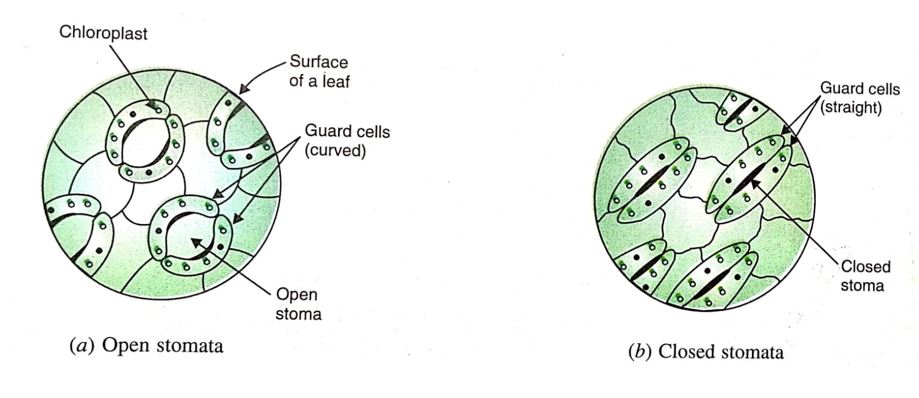
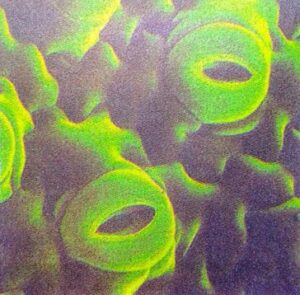
There are a large number of tiny pores called stomata on the surface of the leaves of plants (The singular of stomata is stoma). The green plants take carbon dioxide from air for photosynthesis. The carbon dioxide gas enters the leaves of the plant through the stomata present on their surface. Each stomatal pore (or stoma) is surrounded by a pair of guard cells. The opening and closing of stomatal pores is controlled by the guard cells.
The plants take carbon dioxide required for photosynthesis from air through the stomata (tiny pores) present on the surface of a leaf.
When water flows into the guard cells, they swell, become curved and cause the pore to open. On the other hand, when the guard cells lose water, they shrink, become straight and close the stomatal pore. A large amount of water is also lost from the cells of the plant leaves through open stomatal pores. So, when the plant does not need carbon dioxide and wants to conserve water, the stomatal pores are closed. The oxygen gas produced during photosynthesis also goes out through the stomatal pores of the leaves. Please note that in addition to leaves, the stomata are also present in the green stems (or shoots) of a plant. So, the green stems (or shoots) of a plant also carry out photosynthesis. It is clear from the above discussion that stomata allow the movement of gases in and out of plant cells. In other words, the gaseous exchange in plants takes place through the stomata in leaves (and other green parts).
The stomata on the lower surface of a leaf as seen through a microscope.
Please note that in most broad-leaved plants, the stomata occur only in the lower surface of the leaf but in narrow-leaved plants, the stomata are equally distributed on both the sides of the leaf. Another point to be noted is that the aquatic plants (or water plants) use the carbon dioxide gas dissolved in water for carrying out photosynthesis.
2. How the Plants Obtain Water for Photosynthesis
The water required by the plants for photosynthesis is absorbed by the roots of the plants from the soil through the process of osmosis. The water absorbed by the roots of the plants is transported upward through the xylem vessels to the leaves where it reaches the photosynthetic cells and utilised in photosynthesis.
Water required for photosynthesis is absorbed by the roots of the plants from the soil.
The two raw materials, carbon dioxide and water, are required by the plants to prepare energy foods called carbohydrates (such as glucose and starch). But the plants also need other raw materials such as nitrogen, phosphorus, iron and magnesium, etc., for building their body. The plants take materials like nitrogen, phosphorus, iron and magnesium, etc., from the soil. For example, nitrogen is an essential element used by the plants to make proteins and other compounds. The plants take up nitrogen from the soil in the form of inorganic salts called nitrates (or nitrites), or in the form of organic compounds which are produced by bacteria from the atmospheric nitrogen.
Site of Photosynthesis : Chloroplasts
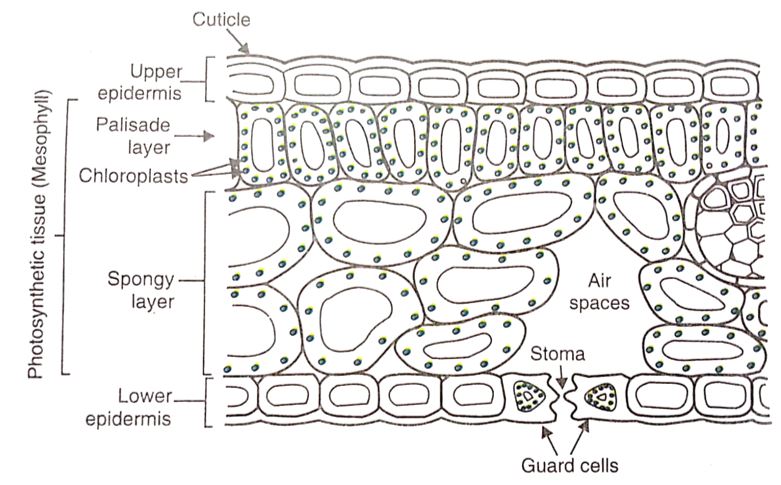
Chloroplasts are the organelles in the cells of green plants which contain chlorophyll and where photosynthesis takes place. Thus, photosynthesis occurs in the organelles called chloroplasts present in the photosynthetic cells (or mesophyll cells) of green plants. In other words, the site of photosynthesis in a cell of the leaf are chloroplasts. Chloroplasts can be seen easily by using a light microscope. In a crosssection of a leaf, chloroplasts can be seen as numerous disc-like organelles in the photosynthetic cells (or mesophyll cells) of the palisade tissue just below the upper epidermis.
The structure of a leaf to show chloroplasts in it (The small green circles in the above diagram are all chloroplasts).
In the structure of a leaf, we can see that the middle layers in the leaf (palisade laver and spongy layer) contain photosynthetic cells called mesophyll cells. These cells contain more, chlorophyll than other plant cells. A typical photosynthetic cell (or mesophyll cell) of a green leaf may contain 100 or more tiny chloroplasts in it, and a whole leaf may contain many thousands of photosynthetic cells, Carbon dioxide needed for photosynthesis enters from the air into the leaf through the stomata in its surface, and then diffuses into the mesophyll cells and reaches the chloroplasts. Water is carried to the leaf by xylem vessels and passes into the mesophyll cells by diffusion and reaches the chloroplasts. There is a thin, waxy protective layer called cuticle above and below a leaf which helps to reduce the loss of water from the leaf.
You can write your questions and suggestions to us in the comment box given below.
Thank you
🌿 Nutrition in Plants – Explained Simply
Nutrition in plants refers to how plants get and use food for growth, energy, and development. Since plants do not move in search of food, they have developed specialized ways to make or absorb nutrients.
🔹 Types of Nutrition in Plants
There are two main types:
1. Autotrophic Nutrition
-
Most green plants follow this.
-
“Auto” means self, “trophic” means nutrition → So, plants make their own food.
-
This happens through Photosynthesis.
-
Example: All green plants (like mango tree, grass, etc.)
2. Heterotrophic Nutrition
-
Some plants depend on other organisms for food.
-
They do not perform photosynthesis (due to lack of chlorophyll).
-
Types:
-
Parasitic: Live on other plants (e.g. Cuscuta or Amarbel)
-
Insectivorous: Trap and digest insects (e.g. Pitcher Plant, Venus Fly Trap)
-
Saprophytic: Feed on dead organic matter (e.g. Fungi, like Mushrooms)
-
Symbiotic: Live in mutual benefit (e.g. Lichens – algae + fungi)
-
🍃 Photosynthesis – The Key Process
Photosynthesis is how green plants make their own food using:
-
Sunlight
-
Carbon dioxide (from air)
-
Water (from soil)
-
Chlorophyll (green pigment in leaves)
Equation:
Or,
🌱 Importance of Nutrition in Plants
-
Helps plants grow and repair tissues.
-
Produces oxygen as a by-product (essential for humans and animals).
-
Provides food at the base of the food chain.
🧠 Quick Revision Points
-
Green plants are autotrophs.
-
Photosynthesis occurs mainly in leaves.
-
Chlorophyll is essential for photosynthesis.
-
Non-green plants follow heterotrophic nutrition.
Would you like a PDF version or a diagram of photosynthesis?