Like animals, plants also need energy. The plants get this energy by the process of respiration. Plants also use oxygen of air for respiration and release carbon dioxide. Thus, the respiration in plants also involves the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide. So, oxygen and carbon dioxide are called respiratory gases. The respiration in plants differs from that in animals in three respects
1. All the parts of a plant (like root, stem and leaves) perform respiration individually. On the other hand, an animal performs respiration as a single unit.
2. During respiration in plants, there is a little transport of respiratory gases from one part of the plant to the other. On the other hand, respiratory gases are usually transported over long distances inside an animal during respiration.
3. The respiration in plants occurs at a slow rate. On the other hand, the respiration in animals occurs at a much faster rate.
Plants get Oxygen by Diffusion
Contents
Plants have a branching shape, so they have quite a large surface area in comparison to their volume. Therefore, diffusion alone can supply all the cells of the plants with as much oxygen as they need for respiration. Diffusion occurs in the roots, stems and leaves of plants.
1. Respiration in Roots
Air is present in-between the particles of soil. The roots of a plant take the oxygen required for respiration from the air present in-between the soil particles by the process of diffusion. The extensions of the epidermal cells of a root are called root hair. The root hair are in contact with the air in the soil. Oxygen (from air in the soil particles) diffuses into root hairs and reaches all the other cells of the root for respiration. Carbon dioxide gas produced in the cells of the root during respiration moves out through the same root hairs by the process of diffusion. Thus, the respiration in roots occurs by the diffusion of respiratory gases (oxygen and carbon dioxide) through the root hairs. It has been found that the land plants die if their roots remain waterlogged for a considerable time. This is because too much water expels all the air from in-between the soil particles. Due to this, oxygen is not available to the roots for aerobic respiration. Under these conditions, the roots will respire anaerobically, producing alcohol. This may kill the plant.
In order to understand the respiration in stems of plants we should remember that the soft stems of small, herbaceous plants have stomata in them whereas the hard and woody stems of large plants and trees have lenticels in them. Lenticel is a small area of bark in a woody stem where the cells are loosely packed allowing the gaseous exchange to take place between the air and the living cells of the stem.
2. Respiration in Stems
The stems of herbaceous plants (or herbs) have stomata. So, the exchange of respiratory gases in the stems of herbaceous plants takes place through stomata. The oxygen from air diffuses into the stem of a herbaceous plant through stomata and reaches all the cells for respiration. The carbon dioxide gas produced during respiration diffuses out into the air through the same stomata. The hard and woody stems of big plants or trees do not have stomata.
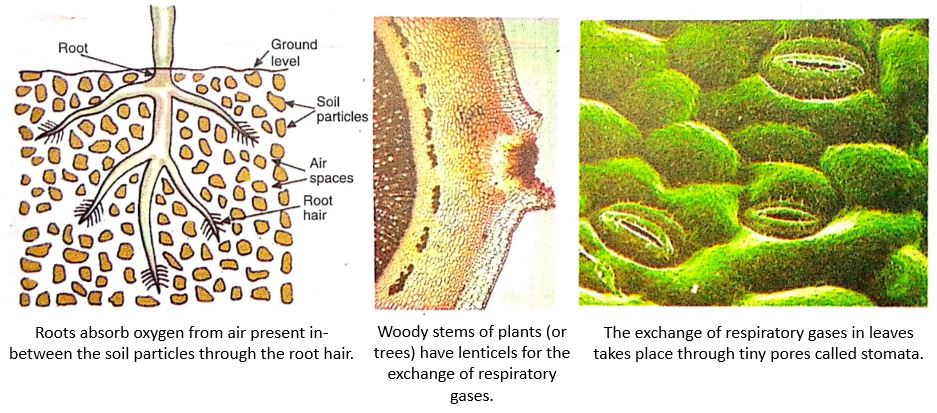
In woody stems, the bark (outer covering of stem) has lenticels for gaseous exchange. The oxygen from air diffuses into the stem of a woody plant through lenticels and reaches all the inner cells of the stem for respiration. The carbon dioxide gas produced in the cells of the stem during respiration diffuses out into the air through the same lenticels.
3. Respiration in Leaves
The leaves of a plant have tiny pores called stomata. The exchange of respiratory gases in the leaves takes place by the process of diffusion through stomata. Oxygen from air diffuses into a leaf through stomata and reaches all the cells where it is used in respiration. The carbon dioxide produced during respiration diffuses out from the leaf into the air through the same stomata.
It should be noted that respiration in leaves occurs during the day time as well as at night. On the other hand, photosynthesis occurs only during the day time (no photosynthesis occurs at night). Due to this, the net gaseous exchange in the leaves of a plant is as follows:
(i) During day time, when photosynthesis occurs, oxygen is produced. The leaves use some of this oxygen for respiration and the rest of oxygen diffuses out into air. Again, during day time, carbon dioxide produced by respiration is all used up in photosynthesis by leaves. Even more carbon dioxide is taken in from air. Thus, the net gas exchange in leaves during day time is : O2, diffuses out; CO2 diffuses in.
(ii) At night time, when no photosynthesis occurs and hence no oxygen is produced, oxygen from air diffuses into leaves to carry out respiration. And carbon dioxide produced by respiration diffuses out into air. So, the net gas exchange in leaves at night is : 02 diffuses in; CO, diffuses out.
You can write your questions and suggestions to us in the comment box given below.
Thank you
Respiration in Plants is a fundamental biological process where plants break down glucose (a sugar) to release energy. Unlike photosynthesis (which stores energy), respiration releases energy that the plant uses for growth, repair, and other life processes.
🌿 What is Respiration in Plants?
Respiration in plants is the oxidation of glucose to release energy (ATP), carbon dioxide (CO₂), and water (H₂O).
General Equation (same as in animals):
C6H12O6+6O2→6CO2+6H2O+Energy (ATP)\text{C}_6\text{H}_{12}\text{O}_6 + 6\text{O}_2 \rightarrow 6\text{CO}_2 + 6\text{H}_2\text{O} + \text{Energy (ATP)}
🔍 Types of Respiration in Plants
1. Aerobic Respiration
-
Occurs in presence of oxygen
-
Complete breakdown of glucose
-
Produces large amount of energy
-
Location: Mitochondria
2. Anaerobic Respiration
-
Occurs in absence of oxygen (e.g. waterlogged soils, yeast cells)
-
Glucose is partially broken down
-
Produces less energy + byproducts (e.g., ethanol or lactic acid)
-
Common in germinating seeds or root cells under stress
🧬 Steps of Aerobic Respiration
-
Glycolysis (in cytoplasm) – Glucose is broken into pyruvate
-
Krebs Cycle (in mitochondria) – Pyruvate is broken down to CO₂
-
Electron Transport Chain – Energy is released to form ATP
🌱 Importance of Respiration in Plants
-
Provides energy for:
-
Cell division
-
Active transport
-
Growth (new cells)
-
Repair of tissues
-
-
Helps in maintaining temperature
-
Balances oxygen and CO₂ in the ecosystem
📊 Differences: Photosynthesis vs Respiration
| Feature | Photosynthesis | Respiration |
|---|---|---|
| Occurs in | Chloroplast | Mitochondria |
| Requires | CO₂, Water, Light | Glucose, Oxygen |
| Produces | Glucose, Oxygen | CO₂, Water, ATP |
| Type of Process | Energy-storing | Energy-releasing |
| Time | Daytime (light needed) | All the time |
🌾 Examples in Daily Life
-
Germinating seeds release heat due to high respiration
-
Waterlogged plants suffer due to lack of oxygen for respiration
-
Storage organs (like tubers) also respire slowly to stay alive
Would you like a PDF version of this explanation, or perhaps questions and answers (Q&A) for school revision?
