We have just studied that digested food is assimilated into the body of the living organisms. The assimilated food is used mainly for two purposes :
1. Assimilated food is used as a fuel to get energy for various life processes, and
2. Assimilated food is used as a material for the growth and repair of the body.
We will now describe how energy is released from the food which is absorbed and assimilated in the cells of the body. Please note that food is the ‘fuel for energy production in cells. Let us see how energy is actually obtained.
Most living things need oxygen (of air) to obtain energy from food. This oxygen reacts with the food molecules (like glucose) present in the body cells and burns them slowly to release energy. The energy thus released is stored in ATP molecules in the cells. The body can use this stored energy whenever it wants to do so.
What is respiration?
Contents
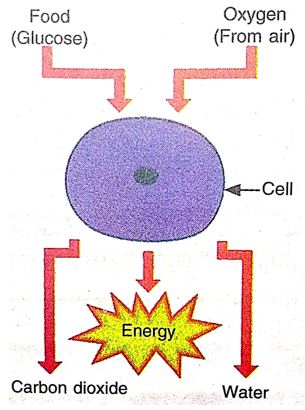
The process of releasing energy from food is called respiration. When oxygen burns the food in the cells of the body to release energy, then carbon dioxide and water are produced as waste products which are to be eliminated from the body.
Respiration takes place in every cell in our body (and those of other organisms). Respiration produces energy from food (like glucose).
The process of respiration involves taking in oxygen (of air) into the cells, using it for releasing energy by burning food, and then eliminating the waste products (carbon dioxide and water) from the body. The process of respiration can be written in the form of a word equation as follows:
Food + Oxygen → Carbon dioxide + Water + Energy
The process of respiration which releases energy takes place inside the cells of the body. So, it is also known as cellular respiration. The process of cellular respiration is common to all the living organisms. It provides energy to the cells. There are two by-products of cellular respiration : carbon dioxide and water. Out of these only carbon dioxide is considered the real waste product of respiration because its accumulation in the body is harmful to the organism. Water produced during respiration is not harmful to the body. It is rather beneficial for the body. Please note that respiration is essential for life because it provides energy for carrying out all the life processes which are necessary to keep the organisms alive.
Breathing and Respiration
The mechanism by which organisms obtain oxygen from the air and release carbon dioxide is called breathing. Respiration is a more complex process. Respiration includes breathing as well as the oxidation of food in the cells of the organism to release energy. Breathing is a physical process whereas respiration also includes biochemical process of oxidation of food. The process of breathing involves the lungs of the organism whereas the process of respiration also involves the mitochondria in the cells where food is oxidised to release energy.
Respiration is actually a biochemical process which occurs in stages and requires many enzymes. The main purpose of respiration is the release of energy from the oxidation of simple food molecules like glucose. The energy released during respiration is used for carrying out the biological functions which are necessary for the maintenance of life and survival of an organism. Please note that respiration is just opposite of photosynthesis. This is because photosynthesis makes food (like glucose) by using carbon dioxide, water and sunlight energy, and releasing oxygen; whereas respiration breaks food (like glucose) by using oxygen, and releasing carbon dioxide, water and energy.
How Energy Released During Respiration is Stored
All the energy released during respiration is not used immediately by an organism (plant or animal). The energy produced during respiration is stored in the form of ATP molecules in the cells of the body and used by the organism as and when required. In order to understand this we should first know the meaning of ADP, ATP and inorganic phosphate. These are given below.
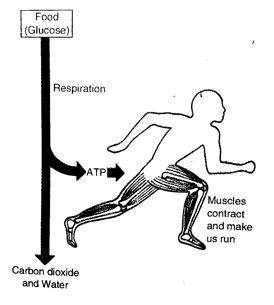
The energy produced from food like glucose during respiration is stored in the form of ATP molecules in the cells of the body. This stored energy can be utilised by the body for various purposes (say, like the contraction of muscles to make us walk or run).
ADP is a substance called Adenosine Di-Phosphate. The molecules of ADP are present in a cell. ADP has low energy content. ATP is a substance called Adenosine Tri-Phosphate. It is also present inside a cell. ATP has a high energy content. Inorganic phosphate is a substance which contains a phosphate group made up of phosphorus and oxygen. Inorganic phosphates are also present in a cell. Inorganic phosphate can be represented by writing just ‘Phosphate’. The inorganic phosphate can also be represented by the symbol Pi (where P stands for phosphate and i for inorganic). ADP contains two phosphate groups whereas ATP contains three phosphate groups in its molecule.
(i) The energy released during respiration is used to make ATP molecules from ADP and inorganic phosphate.
This happens as follows: ADP combines with inorganic phosphate by absorbing the energy released during respiration to form ATP molecules. That is :
ADP (Low energy) + Phosphate + Energy (From respiration) → ATP (High energy)
Thus, energy is stored in the cells in the form of ATP.
(ii) When the cell needs energy, then ATP can be broken down using water to release energy. Thus :
ATP → ADP + Phosphate + Energy (For use in cells)
The energy equivalent to 30.5 kJ/mole is released in this process. The energy released by ATP is used to carry out all the endothermic reactions taking place in the cells.
Please note that ADP can be converted to ATP by absorbing energy produced during respiration, and ATP can be converted back to ADP releasing energy to be used by the cells, again and again. This ensures a continuous supply of energy to the organism.
Just as a battery can provide electrical energy for different purposes such as lighting, heating, running radio and computer, etc., in the same way, the energy stored in ATP is used by the body cells for various purposes like contraction of muscles, conduction of nerve impulses, synthesis of proteins, and many other activities related to the functioning of cells. In fact, ATP is known as the energy currency of cells.
An Important Discussion
In most of the cases, the organisms (plants and animals) carry out respiration by using oxygen (called aerobic respiration). There are, however, some organisms which carry out respiration without using oxygen (called anaerobic respiration). Before we describe aerobic respiration and anaerobic respiration, we should keep the following points in mind which will help us in understanding the two types of respiration.
- Human Digestive System
- Nutrition in Plants
- Nutrition in Animals
- Nutrition in Amoeba
- What are Life Processes
- Human Circulatory System
1. Glucose is C6H12O6. It is a six carbon atom compound. It is the simple food which is oxidised in the cells of organisms during respiration.
2. The oxidation of glucose to pyruvic acid (or pyruvate) is called glycolysis. It occurs in the cytoplasm of a cell and not in mitochondria. The oxidation of glucose to pyruvic acid does not require oxygen. One molecule of glucose on glycolysis produces two molecules of pyruvic acid (or pyruvate).
3. Pyruvic acid is a three carbon atom compound. It is also called pyruvate. The formula of pyruvic acid or pyruvate is
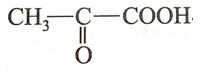
It is a ketonic carboxylic acid.
4. The fate of pyruvate formed during respiration depends on whether oxygen is present in the cells or not. If oxygen is present in the cells, then pyruvate is completely oxidised to carbon dioxide and water, and a lot of energy is produced in the form of ATP). If, however, oxygen is not present in the cells (that is, in the absence of oxygen), pyruvate is converted to either ‘ethanol and carbon dioxide’ or ‘lactic acid’ depending on whether such a process is taking place in a plant cell or an animal cell. Much less energy is released in this case.
5. Lactic acid is also a three carbon atom compound. It is also called lactate. The formula of lactic acid
or lactate is
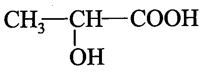
It is a hydroxy carboxylic acid.
You can write your questions and suggestions to us in the comment box given below.
Thank you